The European Union is making history with its groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence Act, the first comprehensive legal framework for AI in the world. This legislation, a cornerstone of the EU's digital strategy, seeks to establish a balanced ecosystem for the development and use of AI, ensuring that it brings numerous social and economic benefits while protecting fundamental rights and security. In the following post, we will analyze some considerations of this regulation that begins to shape the current landscape.
Understanding the Scope and Vision
In April 2023, a first regulatory framework has already been proposed for the European Union, now the developing AI Act is an ambitious attempt by the European Union to regulate artificial intelligence and its applications. It reflects a desire to harness the benefits of AI-improvements in healthcare, safer transportation, more efficient manufacturing, and sustainable energy solutions-while addressing the inherent risks and challenges.
A Risk-Based Approach
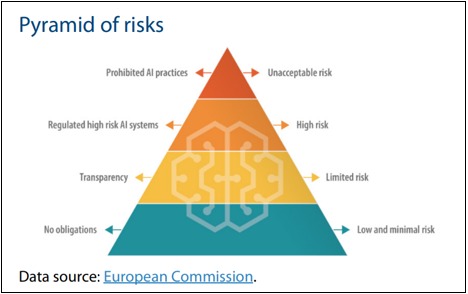
A key feature of the legislation is its risk-based classification of AI systems. This approach categorizes AI applications according to the level of risk they pose to users, with varying degrees of regulation for each category. With a proposal prioritizing ensuring safety, transparency, traceability and environmental stewardship.
This law also aims to establish a uniform definition that can be applied in future systems.
#0 - Unacceptable Risks
The AI Act identifies certain AI practices as 'unacceptable risk' and proposes their prohibition as a threat to people.
These include:
- Cognitive behavioral manipulation of vulnerable groups (e.g., toys that may put children at risk)
- Social scoring systems by governments (We have seen it on Netflix and yes, it is being regulated).
- Real-time remote biometric identification systems (with specific exceptions for significant public interest).
#1 - High Risk Systems
For AI systems considered 'high-risk', the law proposes stringent requirements. These include AI used in safety-critical areas of products (such as aviation and medical devices, automobiles, elevators) and key sectors such as law enforcement, employment and private and public services, education, migration and borders, legal assistance, for these cases a registry will be established.
#2 - Generative AI: Transparency and Accountability
The law requires generative AI systems, such as ChatGPT, to adhere to transparency standards, disclose AI-generated content, prevent the generation of illegal content, and provide information about the data used in their training.
#3 - Limited Risk AI Systems
Limited-risk AI systems must meet minimum transparency requirements to ensure user awareness and informed decision-making. The user must be able to decide to continue using them. The user must be able to recognize that he/she is interacting with the AI, even when using digitally created audio, video, image content (e.g. Deepfakes).
Roadmap
As of June 14, 2023, EU lawmakers have established their negotiating position on the AI Law. Upcoming discussions will shape the final law, with the goal of reaching an agreement by the end of the year. The AI Law represents a delicate balance between encouraging AI innovation and ensuring public safety and rights. It sets a precedent for global AI governance, potentially influencing future regulations worldwide.
Conclusion
While the Act is a step forward, its implementation poses challenges, including ensuring compliance, adapting to technological advances, and balancing the interests of different stakeholders. The EU Artificial Intelligence Act is an important step in the regulation of AI technology. It reflects a commitment to the ethical development of AI, ensuring that the technology serves humanity while safeguarding against its potential dangers.
More information
- EU AI law: first regulation on artificial intelligence(European Parliament)
- Report: Artificial Intelligence Act