In this post we will develop an excerpt from the report “CCN-CERT IA-35/23 Cyber Threats and Trends " which addresses a scenario that we can consider critical in the history of cybersecurity, it focuses on the events of 2022. This being an exceptional period not only because of the start of the armed conflict in Ukraine due to the Russian invasion, but also because of the significant impact these events had on cyberspace.
The unprecedented synergy observed between traditional military operations and cyber operations has been representative, marking a turning point in the nature of modern warfare. Moreover, it highlighted an increase not only in the sophisticated activity of cyberattack groups but also in their level of hostility. This global scenario provided a unique context for understanding how geopolitical events and crises can shape and transform the cyber threat landscape and cybersecurity strategies worldwide.
Some highlights
1- Development of artificial intelligence:
OpenIA with its publication of ChatGPT has given the possibility to all types of public to interact directly with an AI model, there was no delay in identifying the possibilities in the field of cybersecurity (both for protection and for the adversary).
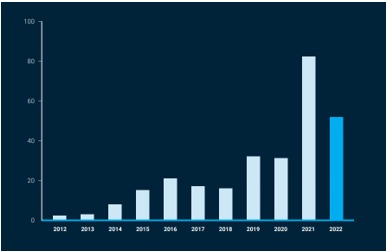
2- Zero-day vulnerabilities:
Although the figures analyzed do not exceed the record, the number of exploited zero-day vulnerabilities has been very high, reaching values much higher than those recorded in 2020 and previous years.
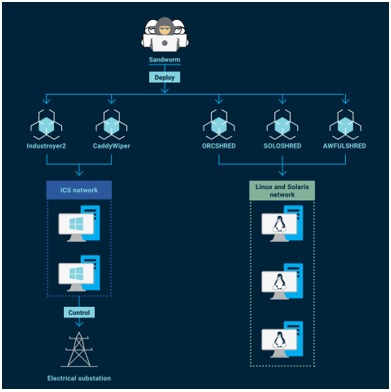
7- Cybercrime During the Pandemic:
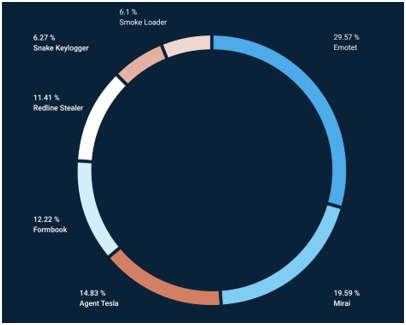
There was a decrease in cybercrime incidents during the pandemic (2020-2022), attributed to the disruption of criminal activities and lack of visibility into user activity. However, there was a notable resurgence in Emotet activity in 2022, with new techniques to evade detection.
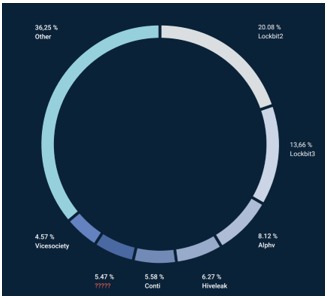
9- Impact of Technological Development and Teleworking:
The rapid technological development and adoption of teleworking during the pandemic created new opportunities for cybercriminals, who began exploiting remote access services and publicly exposed administrative web panels.
10- Rise of Infostealer Malware: There was an increase in the use of infostealer malware (information stealers), with operators offering their use as a service. This type of malware is used to collect sensitive information, such as passwords and cryptocurrency data. Although there are open source infostealer malware families, it is common for different operators to offer their use as a service (malware-as-a-service), with different rental options to suit their customers.
Conclusion
The Cyber Threats and Trends report (CCN-CERT IA-35/23) is further evidence of the dynamic and generally turbulent world of cyberspace in recent years. Through an analysis of events in 2022 and emerging trends in 2023, it is clear that there is a rapid evolution, influenced by geopolitical factors and technological advances. The invasion of Ukraine by Russia not only set a change in the nature of conventional warfare, but also reinforces cyberspace as an active battlefield with new tactics and strategies.
It highlights the importance of "monitoring and detecting", resilience and continuous innovation in the field of cybersecurity. The continued sophistication of cyber-attacks, the innovative use of technologies for espionage and sabotage purposes, and the rise of cybercrime, mixed with the era of teleworking, highlight the need for robust and "multidimensional" security strategies to enhance protections.