We will address a topic that we can consider crucial in the landscape of a cyber-attack: Stealer logs. These logs represent a direct window into our assets and the techniques employed by cybercriminals to reach us. They are often much more than simple collections of data: they are the result of carefully orchestrated operations to infiltrate our systems. We will analyze this concept a little, how it differs from a Data Leak and how it can affect our organizations.
What are Stealer logs?
These are files generated by a specific type of malware known as "Stealer", the "information thief". This malware is designed to infiltrate systems with a clear objective: to obtain sensitive user information.
Once a Stealer is installed on a device, it begins to collect a wide range of data. This can include login credentials, credit card details, browsing histories, cookies, and any other information that can be exploited by cybercriminals. All of this collected data is stored in Stealer logs.
These logs are a goldmine for attackers, as they provide them with direct access to online accounts, financial systems, and personal data. Cybercriminals can use this information to commit fraud, conduct unauthorized financial transactions, or even sell it on the black market.
Types of Stealer logs
These can vary significantly depending on the type of purpose for which they are generated. Although their fundamental purpose is the same - to collect and store sensitive information - the differences lie in the methods of data collection, the type of information they prioritize, and the evasion techniques they employ. Here are some common varieties:
Credentials: These focus on collecting usernames and passwords. They are common in attacks targeting online services such as social networks, email platforms and e-commerce sites.
Financial Data: Specifically designed to capture financial information, such as credit card numbers, bank account details, and transaction data.
Browser Information: Collect data from web browsers, such as browsing histories, cookies, and active session data.
Documents and Files: Search for and extract specific documents, images, and other files stored on the infected device.
Advanced: They combine multiple functions, not only stealing information, but also performing additional actions such as downloading more malware, key logging, or taking screenshots.
Each type of Stealer log represents a unique threat and requires different mitigation strategies. Understanding these varieties helps us develop more effective approaches to protect our systems and data.
Stealer log vs Data Leak
While surfing the Deepweb we came across these concepts What is the difference between a "Data Leak" and a Stealer log?
A data leak occurs when confidential information is accidentally or illicitly exposed to an unsecured environment (depending on the classification of the information). Data leaks can include anything from personal customer data to trade secrets or intellectual property. Data leaks can affect numerous individuals and organizations, leading to loss of trust, reputational damage and possible sanctions.
Common situations include failures in database configuration, exploited vulnerabilities in websites, or simple errors in data handling by employees.
On the other hand, a Stealer log is in principle a file generated by malicious software specifically designed to steal information from an infected device.
Stealers install themselves on a device, usually through deception techniques or by exploiting vulnerabilities, and begin collecting sensitive information. They typically include login credentials, financial details, browsing histories, and other personal data.
The information collected is generally used to initiate criminal activities, such as unauthorized access to accounts or the generation of more complex attacks.
We can find between the two a virtually indistinguishable similarity, until we put both in the light of the Cyber Kill Chain. The attacker's target for the data is different.
Saving the data affected by the Stealer that we could consider directly in the "Exfiltration" tactic, in light of the MITRE ATT&CK matrix we could place it as follows:

Some examples
For our example, we share some data obtained from a Stealer log that exposes data mostly obtained by affecting a browser, for example, through a malicious extension.

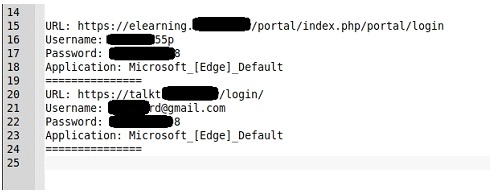
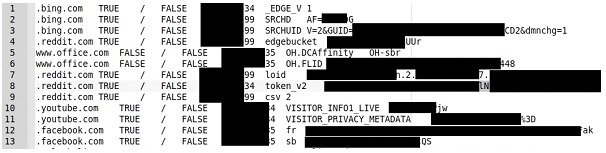
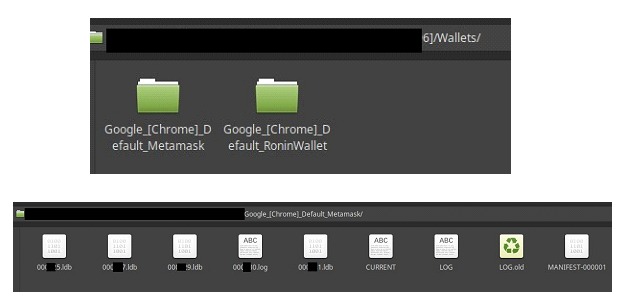
Each of these small logs can provide us with accurate data for collection such as credential sets, cryptocurrency wallets, session cookies or VPN configurations. Or data that we can consider indirect traces such as browsing histories, data copied to clipboards or autocomplete data.
Exploiting logs
Once the records are obtained, the attackers already have "pseudo processes" to exploit each type of data and get the most "benefit", we can list some typical ones such as:
1. Black Market Sales: Information Trading: Stealer logs are often sold on dark markets on the Internet. Cybercriminals trade them to other malicious actors, who can use this information for their own illicit purposes.
2. Direct Access to Online Accounts: Use of Stolen Credentials: The login data obtained is used to access email accounts, social networks, financial services, among others, allowing attackers to commit fraud or identity theft.
3. Financial Fraud: Financial Data Exploitation: With stolen credit card and bank account information, criminals can make fraudulent purchases or drain bank accounts.
4. Social Engineering and Phishing: Manipulation Based on Personal Information: Personal information collected is used to design more convincing phishing attacks or to perform social engineering scams.
5. Extortion and Ransomware: Threats and Coercions: In some cases, if Stealer logs contain particularly sensitive information, criminals may attempt to extort money from victims.
6. Corporate Espionage and Sabotage: In the context of an organization, these may contain valuable information that is used for corporate espionage or sabotage.
7. Sharing with the "community": Stealer logs are also a way for cybercriminals to create a "community", by sharing them they gain a "reputation" that allows them to establish themselves in cyberspace.
Stealer logs are thus powerful tools in the hands of cybercriminals. Their use goes beyond simple information theft; they are breadcrumbs that become the basis for a range of criminal activities, each with its own set of risks and consequences. Prevention, early detection and rapid response are therefore essential to protect our data and systems.